Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tamura, Kazuhisa
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(46), p.22733 - 22739, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)The underpotential deposition of Bi on Au(111) electrode in 1 M HClO solution and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate was investigated using visible light reflectance measurement and surface X-ray scattering techniques. The electrosorption valency of the UPD reaction of Bi was elucidated and it was found that in both 1 M HClO
solution and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate was investigated using visible light reflectance measurement and surface X-ray scattering techniques. The electrosorption valency of the UPD reaction of Bi was elucidated and it was found that in both 1 M HClO and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate the electrosorption valency was smaller than 3, but the detail process in the UPD reaction was different between in two electrolytes. The difference may be originated from the difference in the solvation status of Bi
and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate the electrosorption valency was smaller than 3, but the detail process in the UPD reaction was different between in two electrolytes. The difference may be originated from the difference in the solvation status of Bi rather than the electrical double layer structure.
rather than the electrical double layer structure.
Hirade, Tetsuya; Michishio, Koji*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Oshima, Nagayasu*
Chemical Physics Letters, 795, p.139507_1 - 139507_4, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)We obtained the temperature dependence up to 150 C of the triplet positronium (
C of the triplet positronium (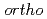 -Ps) lifetime in N,N,N-Trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (TMPA-TFSI) by the vertical slow positron beamline installed at AIST. Positrons penetrate into the liquid surface of TMPA-TFSI with the positron energies of 2 keV and 12 keV to investigate at the near-surface and the balk. The surface structure was visible at 150
-Ps) lifetime in N,N,N-Trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (TMPA-TFSI) by the vertical slow positron beamline installed at AIST. Positrons penetrate into the liquid surface of TMPA-TFSI with the positron energies of 2 keV and 12 keV to investigate at the near-surface and the balk. The surface structure was visible at 150 C, 120
C, 120 C above the melting temperature. The
C above the melting temperature. The 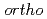 -Ps lifetime became shorter at higher temperatures for both positron energies. Similar temperature dependence had appeared just in water as the result of the reaction of
-Ps lifetime became shorter at higher temperatures for both positron energies. Similar temperature dependence had appeared just in water as the result of the reaction of 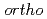 -Ps and radiolysis products such as the OH radicals. The temperature dependence observed for TMPA-TFSI suggested that the chemical reaction of
-Ps and radiolysis products such as the OH radicals. The temperature dependence observed for TMPA-TFSI suggested that the chemical reaction of 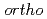 -Ps occurred.
-Ps occurred.
Ueda, Yuki; Eguchi, Ayano; Tokunaga, Kohei; Kikuchi, Kei*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Okamura, Hiroyuki; Naganawa, Hirochika
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 61(19), p.6640 - 6649, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.64(Engineering, Chemical)no abstracts in English
Ito, Tatsuya; Osugi, Haruka*; Osawa, Naoki*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Kim, S.-Y.*; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Analytical Sciences, 38(1), p.91 - 97, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.37(Chemistry, Analytical)A novel ionic liquid (IL) functionalized with thiodiglycol amic acid containing a soft S donor was synthesized for the effective and efficient extraction of platinum group metals (Ru, Rh, and Pd) from aqueous nitric acid solutions, such as high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW). The IL allowed a rapid extraction of Pd(II) with an extraction ratio of approximately 100%. The extractions of Ru(III) and Rh(III) by the IL were slower than that of Pd(II), but the rates were accelerated by temperature elevation. The extractions of Ru(III) and Rh(III) at 50 C reached equilibrium within 4 and 8 h, respectively, with the extraction ratios of over 90% without assisting agents or other methods for the extraction system. Furthermore, the IL could extract more than 90% of Ru(III), Rh(III), and Pd(II) from the simulated HLLW within 2 h at 50
C reached equilibrium within 4 and 8 h, respectively, with the extraction ratios of over 90% without assisting agents or other methods for the extraction system. Furthermore, the IL could extract more than 90% of Ru(III), Rh(III), and Pd(II) from the simulated HLLW within 2 h at 50 C.
C.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Komatsu, Atsushi; Takao, Koichiro*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Watanabe, Masayuki
Chemistry Letters, 50(6), p.1169 - 1172, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.19(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The electrochemical behavior of uranium (IV) tetrachloride in ionic liquid-DMF mixture was studied for first time in order to build a redox flow battery (RFB) using U as an electrode active material. We found a quasi-reversible U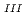 /U
/U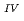 couple that could be applied to the anode reaction of the RFB.
couple that could be applied to the anode reaction of the RFB.
Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Nomizu, Daiki*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Yuji
Hydrometallurgy, 199, p.105539_1 - 105539_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.7(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The synergistic solvent extraction of lanthanide(III) with mixtures of di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (D2EHPA, A) and monoisodecyl phosphoric acid (MIDPA, B) in phosphonium-based ionic liquid was investigated. In the case of D2EHPA or MIDPA single extractant system, Ln(III) (Ln = Pr and Nd) was extracted as [LnA HA] or [LnB
HA] or [LnB HB], respectively, the extracted species of Tb(III) or Dy(III) were determined by slope analysis. According to the equilibrium constants (
HB], respectively, the extracted species of Tb(III) or Dy(III) were determined by slope analysis. According to the equilibrium constants (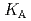 ,
, 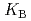 and
and 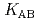 ) and the formation constants (
) and the formation constants (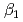 ,
, 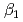 and
and 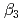 ), it was found that the extracted complex [TbHA
), it was found that the extracted complex [TbHA B
B or [DyHA
or [DyHA B
B ] was more stable than [LnA
] was more stable than [LnA HA] or [LnB
HA] or [LnB HB]. The synergistic extraction effects were investigated to study the possibility of separating Dy(III) from Pr(III) and Nd(III) according to their separation factors.
HB]. The synergistic extraction effects were investigated to study the possibility of separating Dy(III) from Pr(III) and Nd(III) according to their separation factors.
 -diketone extractant and a neutral ligand
-diketone extractant and a neutral ligandMatsumiya, Masahiko*; Nomizu, Daiki*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Yuji
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 39(7), p.764 - 784, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:22.03(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the solvent extraction of four rare earth (RE) elements (Pr, Nd, Tb, and Dy) from Nd-Fe-B magnets using mixtures of 1-(2-thienyl)-4,4,4,-trifluoro-1,3-butanedione (Htta) or 4,4,4-trifluoro-1-phenyl-1,3-butanedione (Hbfa) chelating extractants and tri-n-octylphosphine oxide (TOPO) neutral ligand in phosphonium based ionic liquids. A synergistic effect was observed for the extraction of the RE elements with the combination of extractant and neutral ligand. The separation of Tb(III) and Dy(III) from other RE(III) components was performed with seven extraction cycles.
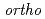 -positronium and radical in liquids
-positronium and radical in liquidsHirade, Tetsuya
Proceedings of 8th Asia Pacific Symposium on Radiation Chemistry (APSRC 2020) (Internet), 2 Pages, 2020/04
The positrons injected in insulating materials make ionization at the end part of the track, forming excess electrons and radicals. When one of the excess electrons and the incident positron form positronium, the electron in the positronium and the unpaired electron in the radical have a spin correlation. By using this spin correlation, a quantum beat phenomenon that depends on the hyperfine coupling constant of the radical appears in the spin conversion reaction with the positronium. The spin-correlated radical and other radicals can be distinguished by a reaction using the positronium as a probe. It is possible to study the behavior of OH radicals in water and the state of cation radicals in room temperature ionic liquids.
Hirade, Tetsuya; Michishio, Koji*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*; Oshima, Nagayasu*
Acta Physica Polonica A, 137(2), p.109 - 112, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Recently, it was reported that the positronium (Ps) bubble in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids (RTILs) showed some phenomena that were very different from them observed in other molecular liquids. Now the reason of these interesting phenomena is being understood. The structure caused by the ionic interaction between anions and cations can exist even at the higher temperatures than the melting temperatures. It was the reason why the oscillation of Ps bubble was observed at the temperatures near the melting temperatures in RTILs. The temperature dependence of the Ps bubble size estimated by the triplet Ps (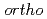 -Ps) pick-off annihilation lifetime indicated that there was a nano-meter structure remained by ionic interactions even at high temperatures. The
-Ps) pick-off annihilation lifetime indicated that there was a nano-meter structure remained by ionic interactions even at high temperatures. The 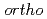 -Ps pick-off annihilation lifetime will be a strong tool to study nano-structure in RTILs.
-Ps pick-off annihilation lifetime will be a strong tool to study nano-structure in RTILs.
Hirade, Tetsuya
AIP Conference Proceedings 2182, p.030007_1 - 030007_5, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:84.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)There are many new application of room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) for many different fields. One of them is reprocessing spent nuclear fuels and then research of irradiation effects on RTILs are very important. The positron annihilation techniques are very strong tool to investigate fast reactions of excess electrons. Positron annihilation age-momentum correlation (AMOC) experiment was applied to deepen understanding the phenomena occurred at very young positron ages. We clarified that Ps bubble formation in RTILs was very slow and, finally, oscillation of Ps bubble was observed just after the Ps formation at near melting temperatures. These results can indicate that Ps formation occurred in very short time in RTILs. The phenomena observed by Ps just in RTILs will be discussed.
Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Cagnes, M.*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Kanaya, Toshiji*; Darwish, T. A.*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 21(32), p.17512 - 17516, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.34(Chemistry, Physical)We combined the deuterium labeling and neutron reflectivity techniques to determine the fine structure of the electric double layer structure in an imidazolium ionic liquid (IL). For this, a simple and large scale deuteration method for imidazolium ILs was developed, where the deuteration level can be systematically controlled.
Hirade, Tetsuya
Yodenshi Kagaku, (11), p.33 - 40, 2018/09
The positron injected in insulating materials thermalizes at the end part of its track and forms Positronium (Ps) with one of excess electrons within  1 ps. Therefore, Ps formation can be a tool to investigate very fast processes like excess electron solvation in liquids. Many phenomena appeared in radiation chemistry researches for room temperature ionic liquids (ILs) are interesting and important for the application. Positron annihilation lifetime (PAL) measurements in ILs were carried out and anomalously long lifetime values of the shortest lifetime component were found in ILs. PAL and positron annihilation age-momentum correlation (AMOC) measurements were performed to clarify the reason of these anomalously long lifetime values and Ps bubble oscillation was finally discovered. Recent progresses are introduced with showing some results.
1 ps. Therefore, Ps formation can be a tool to investigate very fast processes like excess electron solvation in liquids. Many phenomena appeared in radiation chemistry researches for room temperature ionic liquids (ILs) are interesting and important for the application. Positron annihilation lifetime (PAL) measurements in ILs were carried out and anomalously long lifetime values of the shortest lifetime component were found in ILs. PAL and positron annihilation age-momentum correlation (AMOC) measurements were performed to clarify the reason of these anomalously long lifetime values and Ps bubble oscillation was finally discovered. Recent progresses are introduced with showing some results.
Hirade, Tetsuya; O'Rourke, B. E.*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 791(1), p.012029_1 - 012029_4, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We tried to observe the positron annihilation rates near surface of (room temperature ionic liquids) IL's, such as N,N,N-trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (TMPA-TFSI) by use of the perpendicular slow positron beamline installed at AIST. The vaper pressure of TMPA-TFSI is very small and hence it is possible to measure the positron annihilation rate in vacuum chamber directly. This represents the first energy variable experimental results of the positron annihilation rate at the near surface of an IL. The triplet positronium annihilation rate seems to be larger at nearer region to the surface of the IL's.
Hirade, Tetsuya
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 618(1), p.012004_1 - 012004_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:84.11(Physics, Applied)Positronium (Ps; a bound state of positron and electron) has a negative work function in materials and forms a bubble state in liquids. On the way of stable bubble state, the bubble grows and probably oscillates. The usual fast bubble formation has not been observed with the time resolution of the positron annihilation methods that is usually 100-200 pico-seconds. There had been many anomalous phenomena observed in the room temperature ionic liquids (RTIL). Recently it was found that very slow bubble formation caused these anomalous phenomena. And hence the oscillation of the Ps bubble was successfully observed by the change of the annihilation rate of the triplet Ps that is affected by the size of the bubble. The oscillation and the decay of the bubble give the information of the viscoelastic properties at the sub-nano scale. The temperature dependence of the oscillation has been also successfully indicated.
Hirade, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
Positronoum (Ps) has negative work function in insulating materials and the Ps bubbles which size is smaller than a nano meter can form with the repulsion between Ps and surrounding molecules in liquids. Age-momentum correlation (AMOC) measurements of positron annihilation was performed to understand the anomalous positron annihilation lifetime in room temperature ionic liquids (IL), and it was suggested that the Ps bubble formation is anomalously slow in IL. The pick off annihilation rate of ortho-Ps in bubble depends on the size of the bubble. Hence it is probably possible to investigate the slow Ps bubble formation process, such as the bubble oscillation, by observing the ortho-Ps pick off annihilation rate. To obtain the oscillation of the pick-off annihilation rate of ortho-Ps, subtraction of the simulated exponentially decay curve from the measured curve was performed. The oscillation of the ortho-Ps pick-off annihilation rate was successfully observed.
Hirade, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
Ps has a negative work function in insulating materials and the repulsion between Ps and surrounding molecules can form a bubble in liquids. It is needed to lose energy to have a stable bubble state. The Ps bubble stabilizes within about 10 ps in usual liquids, but not in room temperature ionic liquids (IL). It would take about 1 ns in TMPA-TFSI. The ortho-Ps pick off annihilation probability depends on the size of the Ps bubble and hence the change of the ortho-Ps pick-off annihilation rate caused by the change of the bubble size on the lifetime spectra was expected. The results obtained from the lifetime spectra for TMPA-TFSI indicate that the Ps bubble oscillates in IL before the Ps bubble stabilization. On the other hand, the ortho-Ps pick-off annihilation rate obtained at older positron age region showed smaller annihilation rates than the expected one with the surface tension of IL. Positron annihilation methods will be a very strong tool to investigate the structure of IL.
Hirade, Tetsuya; O'Rourke, B. E.*; Kobayashi, Yoshinori*
no journal, ,
A vertical slow positron beam was used to investigate the surface of a room temperature ionic liquid, N,N,N-trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (TMPA-TFSI). Measurement of positron lifetimes indicated a higher Ps formation probability and shorter ortho-Ps annihilation lifetime in near surface of TMPA-TFSI than in the bulk. These changes are probably caused by the layered structure in near surface of TMPA-TFSI. Vertical slow positron beams are a strong tool to investigate the surface of room temperature ionic liquids.
Ueda, Yuki; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Okamura, Hiroyuki; Naganawa, Hirochika; Shimojo, Kojiro
no journal, ,
The separation and recovery of PGM is carried out by a hydrometallurgy process mainly based on a solvent extraction method. In recent years, development of alternative solvents for such volatile organic solvents has been advanced. Ionic liquids (IL) has attracted substantial interest in many fields as a green alternative solvent due to their non-volatile, non-flammable, and thermally stable properties. Task-specific ionic liquids (TSIL) that functionalized by incorporating ligating group can give the extraction ability for metal ions. Many extraction systems using IL and TSIL aimed at separating PGM have been reported so far, however there is no extraction system that achieves individual separation of Pd and Pt by one type of TSIL. In this study, imidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide type TSIL incorporating a urea group was synthesized and its extraction ability for Pd and Pt was evaluated from a viewpoint the individual separation of Pd and Pt.
Hirade, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
The Ps bubble oscillations in N,N,N-trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis(trifluoro-methanesulfonyl)imide (TMPA-TFSI), N-Methyl-N-propylpiperidinium bis(trifluoromethane-sulfonyl) imide (PP13-TFSI) and 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium thiocyanate (EMIM-SCN) were successfully observed. It is almost impossible to see this kind of phenomenon in usual molecular liquids. Even though the Ps bubble size is smaller for EMIM-SCN, the oscillation frequency of the Ps bubble at 10 C above the melting temperatures were quite similar for the other RTILs. Hence, the Ps bubble oscillation is, probably, caused by the repulsive force initiated by the ionic structures in RTILs that can remain at 10-15
C above the melting temperatures were quite similar for the other RTILs. Hence, the Ps bubble oscillation is, probably, caused by the repulsive force initiated by the ionic structures in RTILs that can remain at 10-15 C above the melting temperatures.
C above the melting temperatures.
Ueda, Yuki; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Okamura, Hiroyuki; Naganawa, Hirochika; Shimojo, Kojiro
no journal, ,
Recycling of platinum group metals (PGM) is actively carried out from the viewpoint of stable supply of resources. There are few separating reagents that can separate PGM from each other, and development of a highly selective separating reagent is required. Ionic liquids (IL) are salts with the melting points below 100 degrees Celsius. An ionic liquid can be used as an alternative solvent instead of an organic solvent due to excellent chemical properties such as nonvolatility and nonflammability. In addition, IL can extract charged chemical species and can be functionalized by chemical modification. In this study, we synthesized a novel urea-substituted IL to achieve mutual separation of Pt(IV) and Pd(II). The novel IL synthesized in this study achieved mutual separation of Pt(IV) and Pd(II). Furthermore, spectroscopic analysis of the extraction mechanism revealed that Pt(IV) and Pd(II) were extracted by different extraction mechanisms.